Have you ever noticed that some teeth appear smaller or oddly shaped compared to others? These dental anomalies can sometimes be peg laterals. In this blog, we’ll explore what peg laterals are, their causes, how to identify and treat them, and their impact on your oral health.
Understanding Peg Laterals
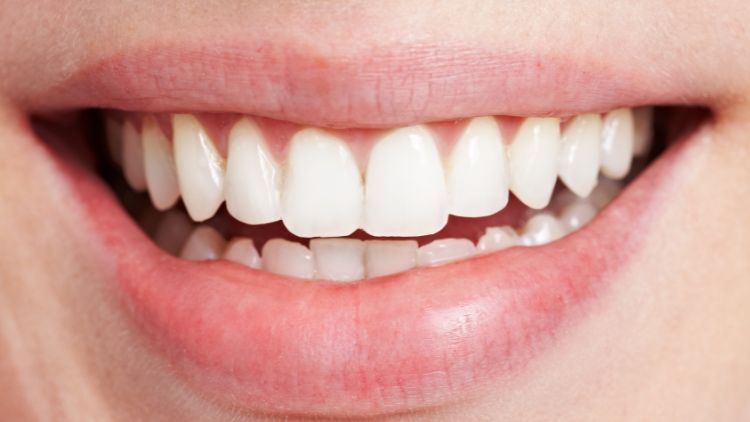
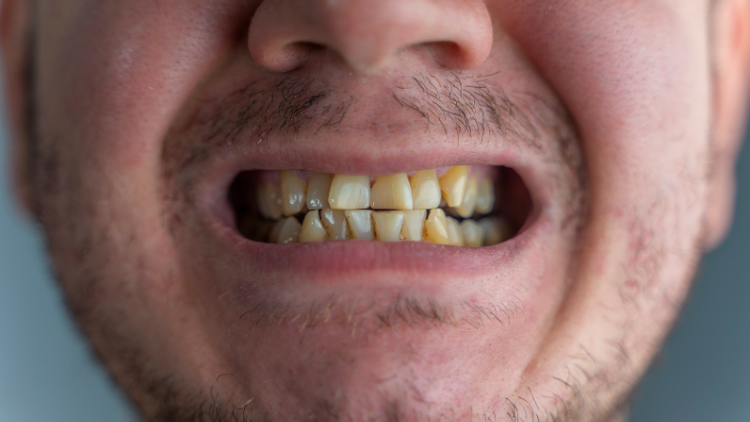
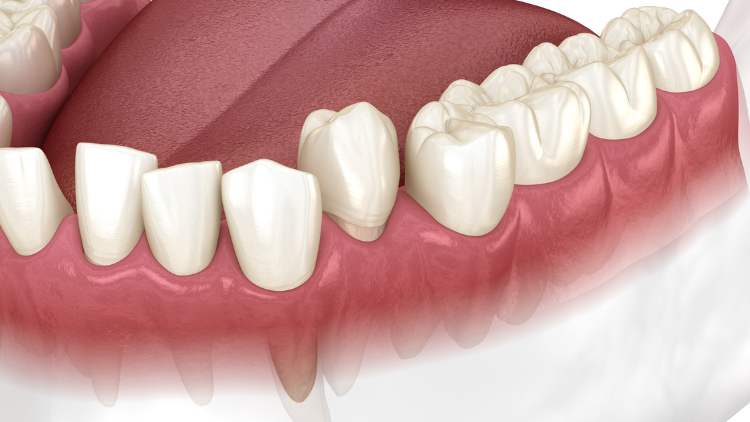
Peg laterals refer to a dental condition where the upper lateral incisors (the teeth next to your front teeth) are smaller and more tapered than usual. Instead of the typical shape and size, these teeth resemble small pegs, hence the name. This condition can affect the appearance of your smile and may sometimes cause functional issues.
Causes of Peg Laterals
Peg laterals are primarily caused by genetic factors. If a parent or close relative has peg laterals, there’s a higher chance that you might have them too. Developmental issues during the formation of teeth can also lead to this condition, but genetics play the most significant role.
Identification and Diagnosis
Identifying peg laterals is relatively straightforward due to their distinctive appearance. These teeth are noticeably smaller and conical compared to the rest of your teeth. However, a proper diagnosis should be done by a dentist. During a dental examination, your dentist will visually inspect your teeth and may use X-rays to get a complete understanding of the tooth structure and any underlying issues.
Impact of Peg Laterals on Oral Health
While peg laterals are often seen as a cosmetic issue, they can also affect your oral health. Here are some potential impacts:
- Aesthetic Concerns: Peg laterals can make your smile look uneven or incomplete, which might affect your confidence.
- Functional Issues: Due to their size and shape, peg laterals can cause spacing issues, leading to bite problems or difficulty in chewing.
- Spacing Problems: The gaps between peg laterals and adjacent teeth can make it easier for food particles to get trapped, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Treatment Options
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available to address peg laterals:
Cosmetic Solutions:
- Dental Bonding: This involves applying a tooth-colored resin to the peg lateral, reshaping it to match the size and shape of your other teeth.
- Veneers: Thin shells of porcelain or composite resin are placed over the peg laterals to improve their appearance and function.
Orthodontic Solutions:
- Braces or Aligners: These can help correct spacing issues and align your teeth properly. In some cases, orthodontic treatment is combined with cosmetic procedures for optimal results.
- Comprehensive Treatment Plans: Your dentist may recommend a combination of orthodontics and cosmetic dentistry to achieve the best possible outcome.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Consider this real-life example: Jane had peg laterals that made her self-conscious about her smile. After consulting with her dentist, she opted for veneers. The transformation was remarkable—her smile became more uniform, boosting her confidence significantly. These success stories highlight how effective treatment can be in improving both appearance and function.
Prevention and Early Detection
While peg laterals are largely genetic and cannot be prevented, regular dental check-ups are crucial. Early detection can lead to more effective and less invasive treatments. If you notice any irregularities in your teeth or your child’s teeth, it’s essential to consult your dentist promptly.
Conclusion
Peg laterals are small, peg-shaped upper lateral incisors that can affect your smile’s appearance and your oral health. While primarily caused by genetics, they can lead to aesthetic and functional issues. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available, from cosmetic solutions like dental bonding and veneers to orthodontic treatments. Regular dental check-ups are key to early detection and effective treatment. request an appointment today!

 Request an Appointment
Request an Appointment