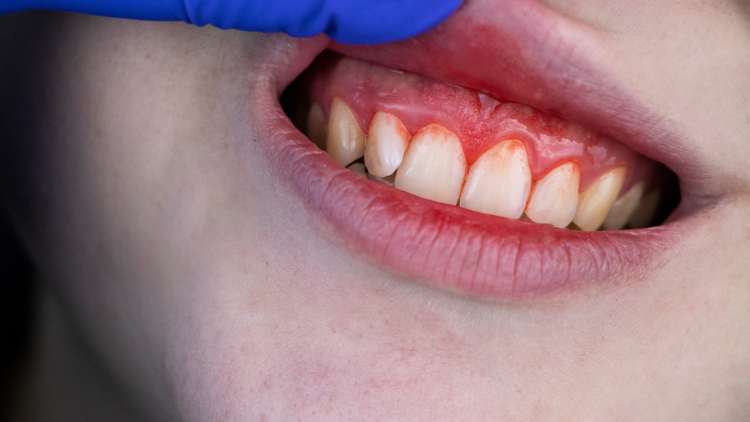
Statistics reveal that a significant portion of the American population, approximately 20%, does not engage in flossing, and merely 4 out of 10 individuals floss daily. Consequently, experiencing bleeding gums during flossing is a prevalent issue for many Americans. While this occurrence might not be uncommon, it is essential to recognize its significance. Bleeding gums could signify underlying gum disease or other dental complications. Seeking professional dental evaluation is crucial to diagnose the root cause and take appropriate action. This article sheds light on the reasons behind bleeding gums and offers insights into effective preventive strategies..
Gingivitis
Bleeding gums may emerge when the accumulation of plaque triggers inflammation and irritation in the gums, leading to bleeding during brushing or flossing. Often, this condition is diagnosed as gingivitis, an initial stage of gum disease. Although gingivitis is typically painless, bleeding gums could serve as the primary symptom. Recognizing gingivitis promptly enhances the potential for its reversal. Gingivitis might manifest as tender and red gums, halitosis, teeth looseness, and misalignment.
Peritonitis
Neglecting gingivitis or the early phases of gum disease can result in gum recession, where the gums separate and pull away from the teeth. This separation creates pockets or gaps between the teeth and gums, providing a breeding ground for trapped bacteria and germs. Bleeding during brushing or flossing is a common occurrence in such cases. Periodontitis is the subsequent stage of gum disease and can lead to tooth and bone loss without proper intervention. Additionally, periodontitis can contribute to abscesses, teeth misalignment, aesthetic changes, and, notably, potential links to diabetes, heart disease, and pregnancy complications.
Other Causes
Less frequent causes of bleeding gums may include nutritional deficiencies, such as inadequate Vitamin C and K intake. Pregnancy can also lead to gum inflammation, resulting in bleeding during oral hygiene practices.
Stopping and Preventing Bleeding Gums
Addressing bleeding gums begins with consulting a dentist to pinpoint the underlying cause and potential gum disease presence. Subsequently, your dentist is likely to recommend a comprehensive approach to restore gum health, including the following strategies:
- Increase frequency of brushing – after meals and before bedtime.
- Utilize toothpaste that is gentle on teeth and gums, contains fluoride, and lacks Sodium Lauryl Sulfate.
- Floss twice daily to maintain oral hygiene.
- Rinse with a recommended mouthwash post brushing.
- Schedule follow-up appointments to monitor gum progress.
Conclusion
The ultimate solution for bleeding gums lies in prevention. Adhering to dental hygiene standards and scheduling regular dentist visits, ideally every six months, significantly reduces the risk of bleeding gums and the onset of gum disease. By upholding strong oral hygiene practices and maintaining a balanced diet, you can effectively diminish the likelihood of bleeding gums and safeguard against gum disease. We are located in Monroe, Michigan. Regain confidence in your smile and contact us today to schedule an appointment.

 Request an Appointment
Request an Appointment